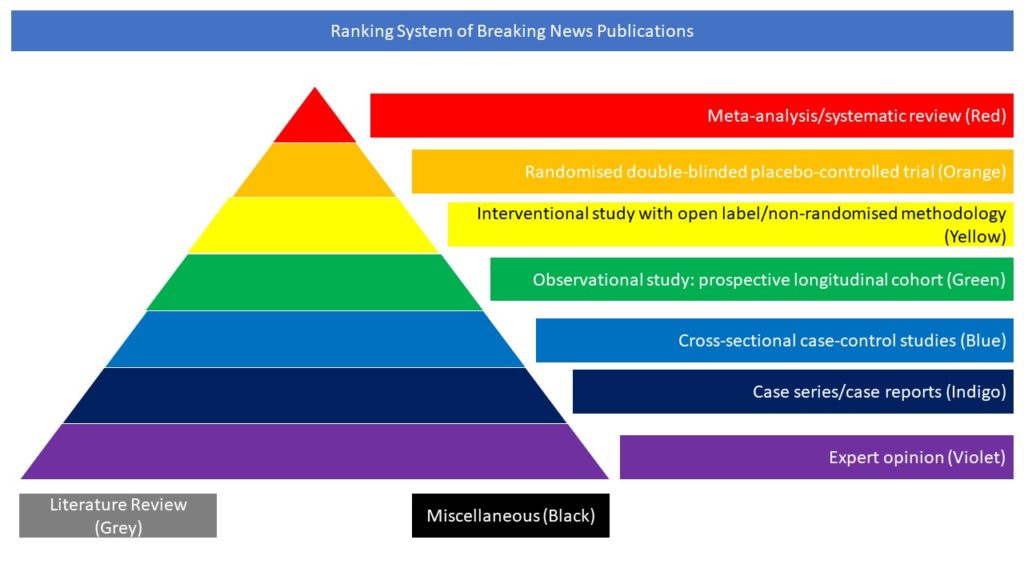
Randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled trial (Orange)
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of bamlanivimab monotherapy and combination therapy with bamlanivimab and etesevimab on SARS-CoV-2 viral load in mild to moderate COVID-19. The BLAZE-1 study is a randomised phase 2/3 trial at 49 US centers including ambulatory patients (N = 613) who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection and had one or more mild to moderate symptom. Patients who received bamlanivimab monotherapy or placebo were enrolled first (June 17-August 21, 2020) followed by patients who received bamlanivimab and etesevimab or placebo (August 22-September 3). Patients were randomised to receive a single infusion of bamlanivimab (700 mg [n = 101], 2800 mg [n = 107], or 7000 mg [n = 101]), the combination treatment (2800 mg of bamlanivimab and 2800 mg of etesevimab [n = 112]), or placebo (n = 156). The primary endpoint was change in SARS-CoV-2 log viral load at day 11 (±4 days). Nine prespecified secondary outcome measures were evaluated with comparisons between each treatment group and placebo, and included 3 other measures of viral load, 5 on symptoms, and 1 measure of clinical outcome (the proportion of patients with a COVID-19–related hospitalisation, an emergency department [ED] visit, or death at day 29). Among the 577 patients who were randomised and received an infusion (mean age, 44.7 [SD, 15.7] years; 315 [54.6%] women), 533 (92.4%) completed the efficacy evaluation period (day 29). The change in log viral load from baseline at day 11 was –3.72 for 700 mg, –4.08 for 2800 mg, –3.49 for 7000 mg, –4.37 for combination treatment, and –3.80 for placebo. Compared with placebo, the differences in the change in log viral load at day 11 were 0.09 (95% CI, –0.35 to 0.52; P = .69) for 700 mg, –0.27 (95% CI, –0.71 to 0.16; P = .21) for 2800 mg, 0.31 (95% CI, –0.13 to 0.76; P = .16) for 7000 mg, and –0.57 (95% CI, –1.00 to –0.14; P = .01) for combination treatment. Among the secondary outcome measures, differences between each treatment group vs the placebo group were statistically significant for 10 of 84 endpoints. The proportion of patients with COVID-19–related hospitalisations or ED visits was 5.8% (9 events) for placebo, 1.0% (1 event) for 700 mg, 1.9% (2 events) for 2800 mg, 2.0% (2 events) for 7000 mg, and 0.9% (1 event) for combination treatment. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 9 patients (6 bamlanivimab, 2 combination treatment, and 1 placebo). The authors concluded that among nonhospitalised patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 illness, treatment with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, compared with placebo, was associated with a statistically significant reduction in SARS-CoV-2 viral load at day 11; no significant difference in viral load reduction was observed for bamlanivimab monotherapy. Further ongoing clinical trials will focus on assessing the clinical benefit of antispike neutralising antibodies in patients with COVID-19 as a primary endpoint.