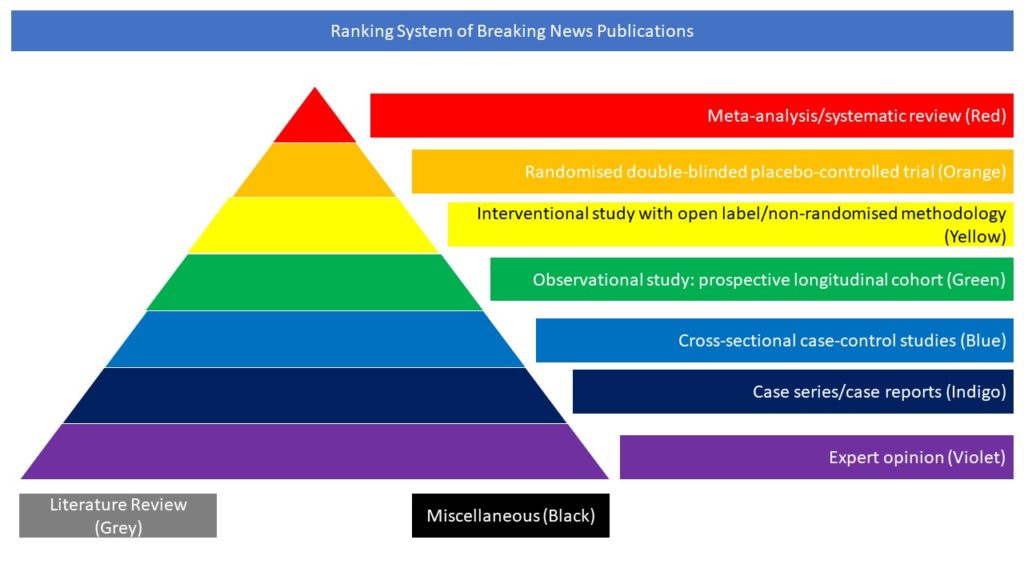
Cross-sectional case-control studies (Blue)
Although infection with SARS-CoV-2 has pleiotropic and systemic effects in some individuals, many others experience milder symptoms. In this article, in order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the distinction between severe and mild phenotypes in the pathology of COVID-19 and its origins, the authors performed a whole-blood-preserving single-cell analysis protocol to integrate contributions from all major immune cell types of the blood—including neutrophils, monocytes, platelets, lymphocytes and the contents of the serum. Patients with mild COVID-19 exhibit a coordinated pattern of expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) across every cell population, whereas these ISG-expressing cells are systemically absent in patients with severe disease. Paradoxically, individuals with severe COVID-19 produce very high titres of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and have a lower viral load compared to individuals with mild disease. Examination of the serum from patients with severe COVID-19 shows that these patients uniquely produce antibodies that functionally block the production of the ISG-expressing cells associated with mild disease, by activating conserved signalling circuits that dampen cellular responses to interferons. Overzealous antibody responses pit the immune system against itself in many patients with COVID-19, and perhaps also in individuals with other viral infections. The authors concluded that their findings reveal potential targets for immunotherapies in patients with severe COVID-19 to re-engage viral defence.